Ultimate Guide to Multi-Currency Accounting for Small Businesses | Giddh

As global trade continues to expand, small businesses are increasingly engaging in cross-border transactions. Recent studies show that over 60% of small businesses are now involved in international commerce, whether through e-commerce, sourcing materials from global suppliers, or servicing international clients.
To navigate this complex landscape, multi-currency accounting has become a critical tool for maintaining financial accuracy and compliance.
But how do businesses ensure they’re managing these transactions efficiently? Multi-currency accounting enables companies to efficiently track, convert, and report on transactions in multiple currencies within a single, unified system. This not only improves financial reporting but also enhances cash flow management and customer satisfaction.
If your business deals with multiple currencies, understanding how to implement and manage this system effectively is crucial. Are you ready to streamline your financial operations and expand globally? Let's dive into the essentials of multi-currency accounting.
What is Multi-Currency Accounting?
Multi-currency accounting is a sophisticated financial management approach that enables businesses to record, track, and report transactions in multiple currencies within a unified accounting system.
Unlike traditional single-currency accounting, this method allows companies to maintain accurate financial records when operating across international borders or dealing with foreign customers and suppliers.
At its core, a multi-currency accounting solution involves three fundamental processes:
- Transaction Recording: Capturing financial transactions in their original currencies.
- Currency Conversion: Converting foreign currency amounts to the company's base currency using appropriate exchange rates.
- Financial Reporting: Presenting consolidated financial statements that accurately reflect the company's global financial position.
Why Small Businesses Need Multi-Currency Accounting
The global marketplace has made international business accessible to companies of all sizes. Small businesses today regularly engage in cross-border transactions that require sophisticated currency management capabilities.
Growing International Business Trends
According to recent studies, over 60% of small businesses now conduct some form of international business, whether through:
- E-commerce sales to international customers
- Sourcing materials from overseas suppliers
- Providing services to global clients
- Operating satellite offices in different countries
What are the Benefits of Multi-Currency Accounting
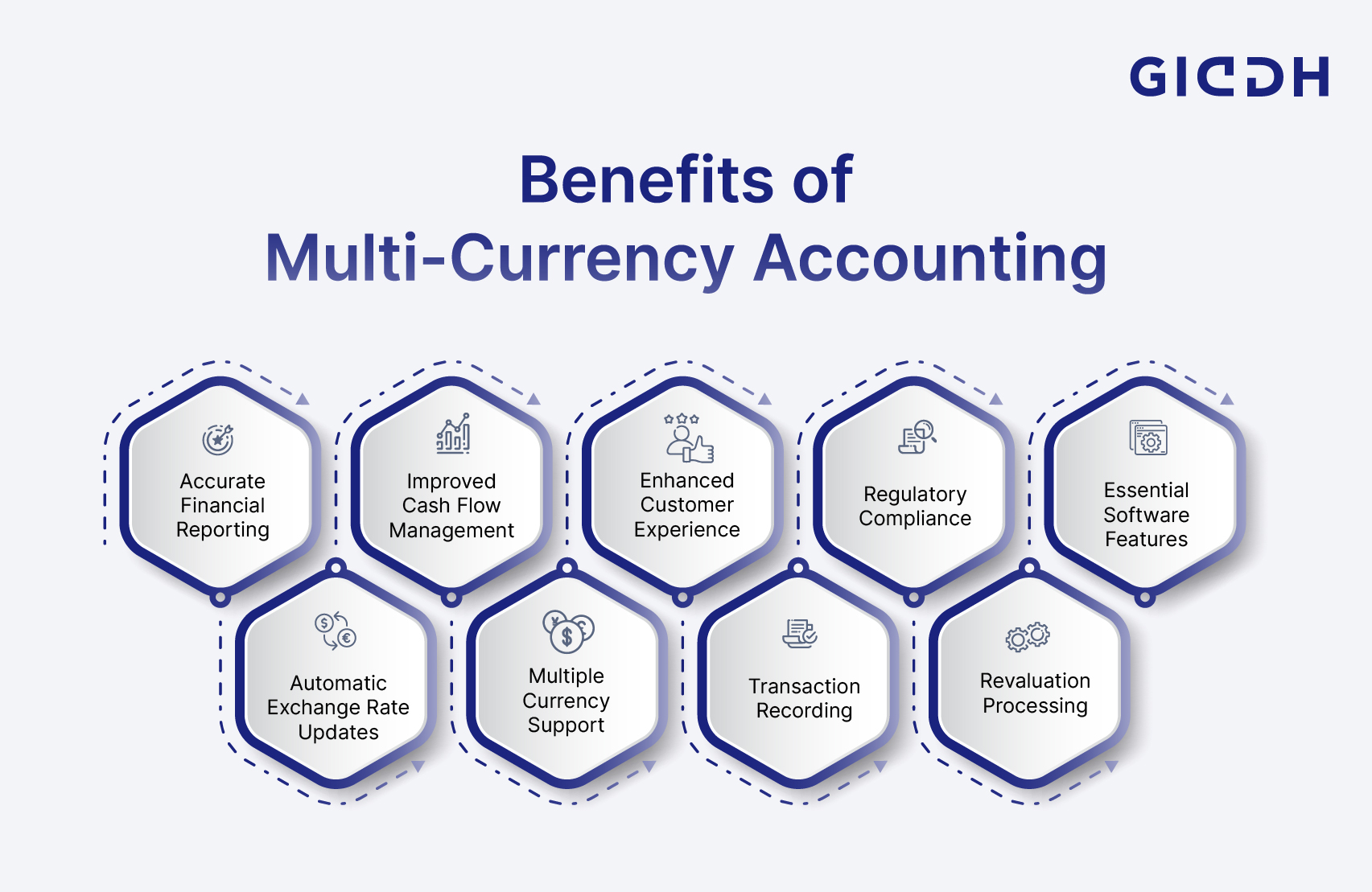
Accurate Financial Reporting
Maintain precise financial records across all currencies, ensuring accurate profit and loss calculations and balance sheet reporting.
Improved Cash Flow Management
Better visibility into foreign currency receipts and payments helps optimize cash flow and reduce currency exposure risks.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Invoice customers in their preferred currencies, improving satisfaction and reducing payment friction in international transactions.
Regulatory Compliance
Meet international accounting standards and local regulatory requirements for businesses operating across multiple jurisdictions.
Essential Software Features
Selecting the best accounting software is crucial for effective multi-currency management. Look for these essential features when evaluating solutions.
Automatic Exchange Rate Updates
Real-time or scheduled updates from reliable financial data sources, with manual override capabilities for specific transactions.
Multiple Currency Support
Support for unlimited currencies with proper currency symbols, decimal places, and formatting rules.
Transaction Recording
Ability to record transactions in original currencies while automatically calculating base currency equivalents.
Revaluation Processing
Automated period-end revaluation of foreign currency balances with gain/loss calculations and posting.
Advanced Features Of Multi-Currency Accounting Software for Growing Businesses
Multi-Currency Invoicing
Professional invoicing software capabilities that include:
- Customer-preferred currency selection.
- Automatic currency conversion at invoice creation.
- Multi-currency payment tracking.
- Currency-specific payment terms.
Comprehensive Reporting
Robust reporting features for multi-currency operations:
- Financial statements in multiple currencies.
- Currency exposure reports.
- Exchange rate variance analysis.
- Consolidated reporting across currencies.
Integration Capabilities
Seamless integration with essential business systems:
- Banking and payment platforms.
- E-commerce and CRM systems.
- Inventory management tools.
- Business intelligence platforms.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Learning from common pitfalls can save your business significant time, money, and compliance issues. Here are the most frequent mistakes in multi-currency accounting and how to avoid them.
Exchange Rate Management Errors
Using Inconsistent Exchange Rates
Mistake: Using different exchange rates for the exact date or transaction type.
Solution: Establish clear policies for rate sources and update them regularly. Use software that maintains rate consistency across all transactions.
Ignoring Rate Date Significance
Mistake: Using current exchange rates for historical transactions or failing to use transaction-date rates.
Solution: Always use appropriate rates based on transaction timing and accounting standards requirements.
Financial Reporting Issues
Inadequate Currency Gain/Loss Recognition
Mistake: Failing to recognize or categorize currency gains and losses properly.
Solution: Implement automated revaluation processes and clearly understand the difference between realized and unrealized gains/losses.
Poor Documentation
Mistake: Insufficient documentation of exchange rates used, conversion methods, and rationale for accounting treatments.
Solution: Maintain comprehensive audit trails and document all currency-related decisions and policies to ensure transparency and accountability.
Operational Mistakes
Manual Process Dependencies
Mistake: Relying too heavily on manual calculations and spreadsheet-based processes.
Solution: Invest in proper accounting software with built-in multi-currency capabilities and automation features.
Lack of Regular Monitoring
Mistake: Not regularly monitoring currency exposures and their impacts on financial performance.
Solution: Establish regular review processes and utilize dashboards for ongoing monitoring of currency exposure.
Why Giddh is Perfect for Multi-Currency Accounting?
Managing multi-currency accounting can be a complex task, but with the right tools, small businesses can easily navigate this challenge. Giddh, an innovative cloud-based accounting software, is designed specifically to simplify multi-currency accounting. With Giddh, you can:
-
Track Transactions in Multiple Currencies: Effortlessly record and manage transactions across various currencies, all within one unified system.
-
Real-Time Exchange Rate Updates: Giddh automatically pulls up-to-date exchange rates, ensuring accurate conversions for every transaction.
-
Streamlined Financial Reporting: Generate consolidated financial statements in your preferred base currency, without manually calculating conversions.
-
Tax Compliance & Regulatory Support: Stay compliant with international standards and local tax regulations by utilizing Giddh’s automated multi-currency features.
-
Seamless Integration: Giddh integrates with your existing systems (e.g., e-commerce platforms, CRMs) to ensure smooth operations across your business.
Whether you’re dealing with cross-border clients or suppliers, Giddh makes multi-currency accounting easy and reliable. Ready to simplify your accounting process? Try Giddh today!
Getting Started: Step-by-Step Guide
Ready to implement multi-currency accounting in your business? Follow this comprehensive step-by-step guide to ensure a smooth transition.
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (Week 1-2)
Step 1: Evaluate Current Needs
- Analyze your current international business activities.
- Identify all currencies you currently use or plan to use.
- Assess transaction volumes and frequency by currency.
- Review existing accounting processes and identify gaps.
Step 2: Choose Your Accounting Software
- Evaluate software options based on your specific needs.
- Consider scalability, integration capabilities, and user-friendliness.
- Review pricing models and total cost of ownership.
- Test software with trial versions or demos.
Phase 2: Setup and Configuration (Week 3-4)
Step 3: Configure Currency Settings
- Set up all required currencies in your accounting system.
- Configure exchange rate sources and update frequencies.
- Establish your functional and presentation currencies.
- Set up currency-specific account structures.
Step 4: Data Migration
- Export existing financial data from current systems.
- Convert historical data to appropriate currency formats.
- Import data into the new multi-currency system.
- Verify data accuracy and completeness.
Phase 3: Implementation and Testing (Week 5-6)
Step 5: Process Integration
- Set up automated workflows for multi-currency transactions.
- Configure invoicing templates for different currencies.
- Establish approval processes for currency-related transactions.
- Train staff on new processes and software features.
Step 6: Testing and Validation
- Process test transactions in multiple currencies.
- Verify exchange rate calculations and conversions.
- Test reporting functionality and financial statement generation.
- Validate compliance with accounting standards.
Phase 4: Go-Live and Optimization (Week 7+)
Step 7: Launch Operations
- Begin processing live multi-currency transactions.
- Monitor system performance and user adoption.
- Address any issues or questions promptly.
- Maintain close oversight during initial weeks.
Step 8: Ongoing Optimization
- Regular review of currency exposure and performance.
- Continuous process improvement based on user feedback.
- Stay updated with accounting standard changes.
- Expand capabilities as business grows.
Conclusion
Multi-currency accounting is no longer just a nice-to-have feature for small businesses—it's becoming essential for companies looking to compete in the global marketplace. By understanding the fundamentals, implementing best practices, and choosing the right technology, your business can confidently manage international transactions while maintaining accurate financial records and regulatory compliance.
The key to success lies in proper planning, choosing the right tools, and maintaining disciplined processes. With the right approach, multi-currency accounting software becomes a competitive advantage that enables your business to serve international customers, work with global suppliers, and confidently expand into new markets.
Remember that multi-currency accounting is an ongoing process that requires regular attention and optimization. Stay informed about accounting standard updates, monitor your currency exposures, and continuously improve your processes as your business grows and evolves.
For more insights on accounting best practices and business growth strategies, explore our comprehensive business accounting resource centre.
FAQ:
1. How To Ensure Accurate Currency Conversions In Accounting Software?
To ensure accurate currency conversions in accounting software, choose a platform that updates exchange rates automatically in real-time. Always verify that the software supports multiple currencies and integrates with trusted financial sources or APIs. Double-check your base currency and ensure consistent updates for exchange rates to avoid discrepancies.
2. How Can Small Businesses Seamlessly Manage Multi-Currency Accounting?
Small businesses can manage multi-currency accounting by using specialized software that automates currency conversion, generates real-time exchange rate updates, and allows seamless integration with payment gateways. Ensure that the software provides a unified dashboard for easy tracking of foreign transactions.
3. How Does Accounting Software Handle Multi-Currency Transactions?
Accounting software handles multi-currency transactions by automatically converting currencies based on real-time exchange rates. It records each transaction in the appropriate currency and provides consolidated reports, ensuring tax compliance and reducing manual errors.