Types of Billing Systems: Which One Fits Your Business Best?

Recent research shows that nearly 58% of mid‑sized businesses lose revenue due to billing errors and delayed payments. These operational gaps directly impact cash flow, customer trust, and growth momentum. When your business still relies on spreadsheets or manual tracking, simple mistakes such as misapplied taxes or duplicate invoices are far too common.
For businesses in India, especially, GST compliance adds another layer of complexity that basic tools often fail to handle reliably. With rising customer expectations and tightening regulatory frameworks, identifying the right billing systems is no longer a back‑burner task.
This comprehensive guide explains:
-
What are billing systems?
-
The different types of billing systems available.
-
Pros, cons, and best fit for each.
-
How to choose the right system for your business operations.
Whether you’re evaluating billing software online, a GST‑ready solution, or a full billing‑plus‑accounting suite, you’re in the right place.
What Are Billing Systems? A Quick Overview
Billing systems are tools and platforms designed to generate invoices, track payments, and manage receivables. At their core, they help businesses:
-
Create accurate invoices.
-
Track unpaid and overdue bills.
-
Monitor customer payment history.
-
Integrate with tax and compliance processes.
A billing management system can range from a simple invoicing template to a full‑featured automated platform that ties into accounting, inventory, and banking. The key difference lies in scope and automation:
-
Basic invoicing tools handle individual bills but lack deeper process integration
-
Complete billing management systems automate tax calculations, reminders, reporting, and reconciliation.
Getting this right reduces errors, saves time, and improves financial visibility across your business.
Types of Billing Systems Explained (Core Comparison)
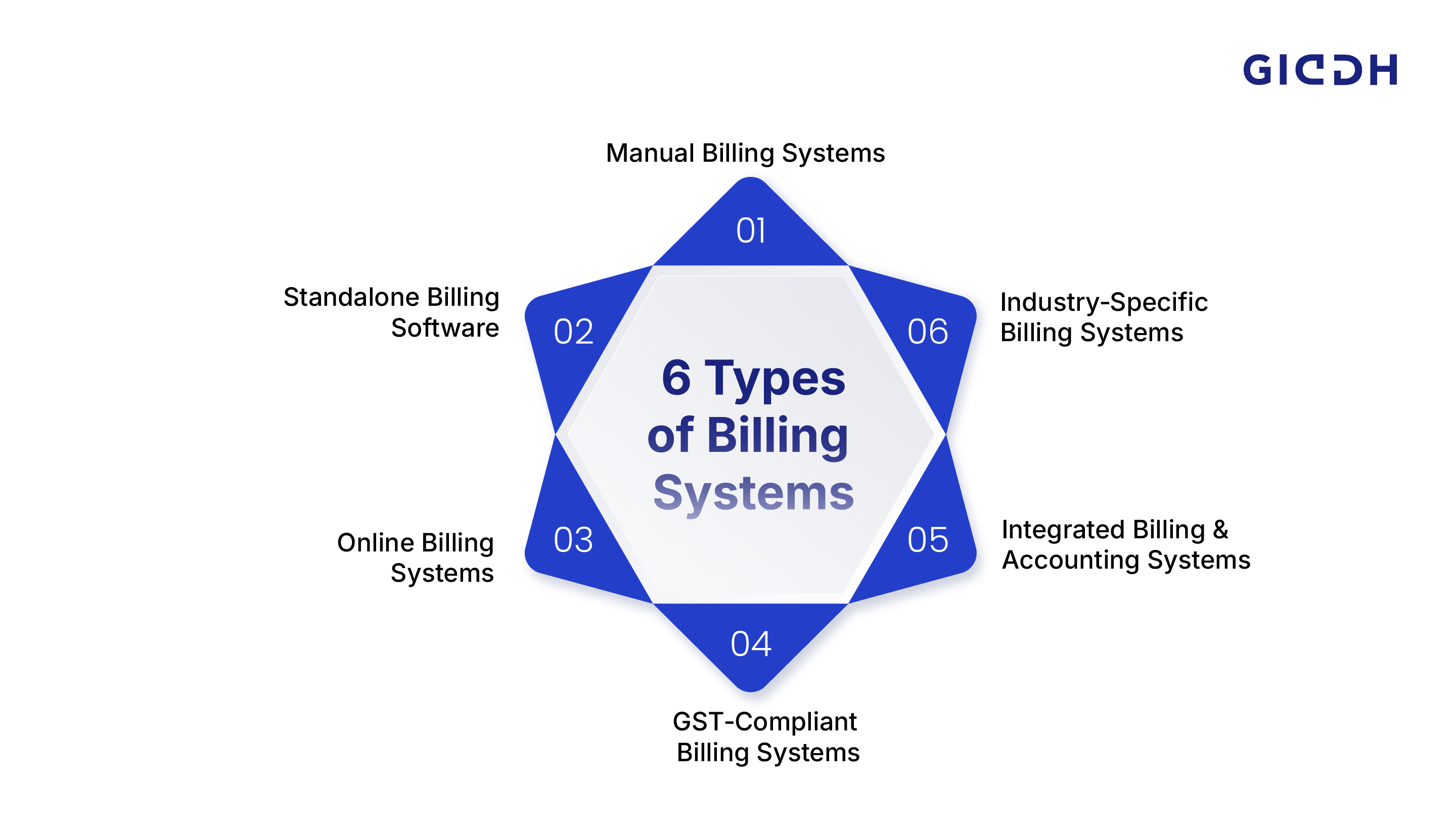
This section breaks down the most common types of billing systems you’ll encounter. We highlight how each works, its strengths, limitations, and best use cases.
Manual Billing Systems (Spreadsheets & Offline Methods)
How they work:
Manual billing relies on spreadsheets, templates, or paper‑based invoices. Teams manually enter customer details, calculate totals, apply taxes, and track payments.
Pros:
-
Low upfront cost.
-
Simple to set up.
-
Familiar to most teams.
Cons:
-
High risk of human error.
-
No automated reminders.
-
Difficult to scale.
-
No real‑time visibility into receivables.
Best for: Very early‑stage operations with minimal billing volume.
Manual systems might work for the very start, but businesses quickly outgrow them once invoice volume increases or compliance requirements tighten.
Standalone Billing Software
These are packaged tools explicitly designed for invoicing, typically installed on a computer. They generate bills and sometimes offer basic customer and product records.
Pros:
-
Quick invoice creation.
-
Affordable entry point.
-
Better formatting than manual templates.
Cons:
-
Limited automation.
-
Few integrations with banks or accounting tools.
-
Often does not handle tax logic automatically.
Best for: Small businesses with infrequent invoicing and simple requirements.
Standalone software helps reduce some manual effort, but without automation, it still requires regular oversight.
Online Billing Systems (Cloud‑Based)
Cloud billing systems are accessed through the internet. They store billing data on secure servers and allow multiple users to access it from any location.
Benefits:
-
Real‑time access from anywhere.
-
Automated workflows (e.g., recurring invoices).
-
Multi‑user collaboration.
-
Data is stored securely with backups.
Limitations:
-
Requires internet connectivity.
-
Monthly subscription costs.
Best for: Growing startups and distributed teams that need visibility and collaboration.
Cloud systems eliminate manual sync issues. They automate reminders, track payment status in real time, and give finance teams better control without juggling multiple spreadsheets.
GST‑Compliant Billing Systems
In India, GST compliance isn’t optional. A GST‑ready billing system automatically applies correct tax rates, generates compliant invoices, and supports mandatory reporting requirements.
Key Capabilities:
-
GST tax calculation.
-
HSN/SAC code support.
-
E‑invoice and GST return readiness.
-
Tax summary reports.
Advantages:
-
Fewer compliance errors.
-
Accurate tax filing support.
-
Consistency across states.
Suitable for: GST‑registered entities and businesses with significant tax complexity.
For businesses dealing with GST, a GST‑aware billing system is virtually mandatory. It eliminates tax‑driven errors before they become regulatory issues.
Integrated Billing & Accounting Systems
These platforms go beyond billing. They unify invoicing with accounting features, so every invoice, payment, and adjustment is reflected consistently in financial books.
Benefits:
-
Auto‑sync between billing and ledgers.
-
Better cash flow forecasting.
-
Centralized tax, payments, and reporting.
-
Reduced reconciliation effort.
Drawbacks:
-
Higher setup complexity.
-
Slightly steeper learning curve.
Best for: Mid‑sized businesses scaling operations and requiring deeper financial visibility.
Integrated systems give finance teams a single source of truth. They reduce duplicate entries and eliminate data gaps.
Industry‑Specific Billing Systems
Some businesses have unique billing requirements: subscription models, service billing, usage‑based pricing, or retail tied to inventory.
Examples:
-
Subscription billing for SaaS businesses.
-
Service‑based billing with time and expense tracking.
-
Retail billing systems integrated with POS and stock.
Pros:
-
Tailored workflows.
-
Optimized for specific billing patterns.
Cons:
-
It can be expensive.
-
It may be too niche for broad use.
Best for: Industries with specialized pricing structures.
These solutions make billing more efficient when standard tools cannot adapt to specific patterns, such as recurring usage or complex service charges.
Billing Systems for Small Business: What Actually Works
Small businesses often start with limited budgets and modest invoice volumes. Their top challenges include:
-
Manual errors from data entry
-
Late payments due to a lack of reminders
-
Compliance with GST and taxes
-
Poor visibility into receivables
Must‑have features for small business billing:
-
Automated invoice generation
-
Customer payment tracking
-
GST tax handling
-
Online access for remote management
-
Integration with bank feeds and accounting
When to upgrade:
-
Invoice volume rises above ~50/month
-
You start offering credit terms.
-
GST compliance becomes a regular headache
-
You need reporting, not just invoices.
A cloud‑based, GST‑ready billing solution delivers the right balance of automation, compliance, and scale.
How to Choose the Right Billing System for Your Business
This section helps you evaluate systems with a decision framework.
Key Factors to Evaluate
Invoice Volume:
Higher volumes demand automation and reminders.
GST and Tax Needs:
If GST is central to your invoicing, choose a system that calculates and reports taxes accurately.
Team Size:
Multiple users require cloud access and role‑based permissions.
Integration Needs:
Billing that works with accounting, CRM, and banking saves time.
Evaluation Checklist
Use this checklist when comparing billing solutions:
-
Level of automation
-
GST tax readiness
-
Reporting and analytics
-
User roles and multi‑access
-
Backup and security
-
Cost vs long‑term value
This framework also prepares you to download and use our Billing System Comparison Guide for a deeper side‑by‑side comparison.
Where Giddh Fits In: A Smarter Billing System for Growing Businesses
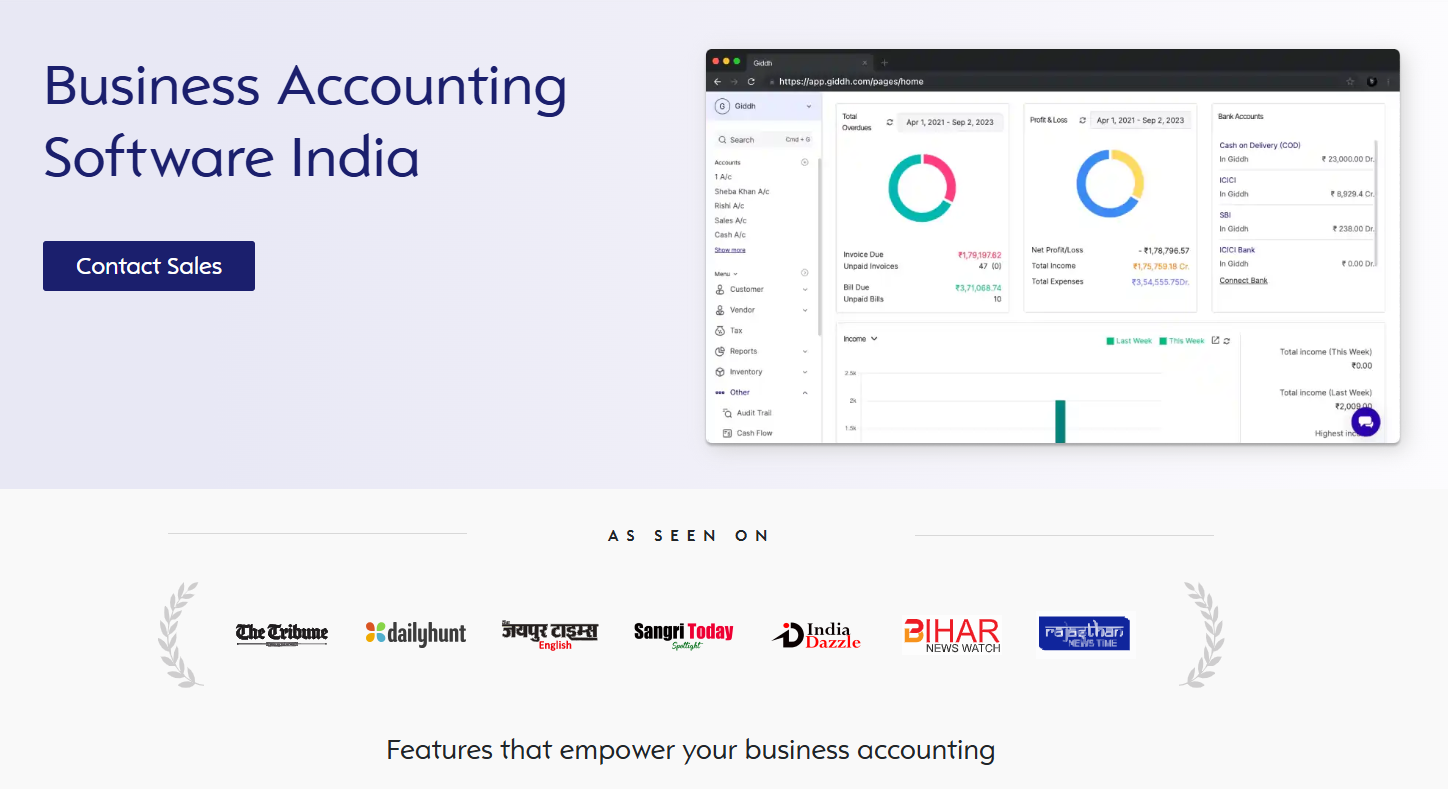
Giddh is a cloud‑based billing and best accounting platform designed to help mid‑sized businesses and startups shift from manual processes to automated finance workflows. It combines billing, GST compliance, and real‑time accounting in a single system.
What makes Giddh effective:
-
GST‑compliant invoicing with built‑in tax logic
-
Automated reminders to drive timely payments
-
Real‑time sync between billing and accounting ledgers
-
Multi‑user access for finance and operations teams
-
Secure cloud storage with backups and audit trails
Who benefits most:
-
Small businesses ready to scale
-
Mid‑sized businesses needing compliance and control
-
Teams are moving beyond spreadsheets but are not ready for heavy ERP systems.
With Giddh, finance teams spend less time fixing errors and more time analyzing performance.
Common Billing System Mistakes Businesses Make
Investing in billing systems is valuable, but selecting the wrong type wastes time and money.
Mistake #1: Choosing Tools That Only Do Billing
Billing alone doesn’t give a full financial view—integration with accounting matters.
Mistake #2: Ignoring GST Compliance
Non‑GST‑ready systems require manual tax adjustments and are prone to errors.
Mistake #3: Overlooking Scalability
A system that works today may fail as you grow.
Mistake #4: Delaying Automation
Manual billing seems cheap, but it drains time and causes errors.
Avoiding these traps keeps your billing process efficient and future‑ready.
Conclusion
Billing isn’t a back‑office footnote anymore—it’s central to healthy cash flow, compliance, and customer trust. The right billing systems remove manual burden, reduce errors, and help finance teams stay in control.
Your choice should match your business maturity:
-
Start simple and affordable
-
Scale to cloud and GST compliance
-
Move to integrated billing‑plus‑accounting as complexity grows
Invest the time now to evaluate systems with clarity. Use the comparison frameworks here and in our Billing System Guide to make the right decision.
👉 Download Giddh for free and equip your finance team with a solution that fits your business today and tomorrow.
FAQ —
Q1. What are the different types of billing systems?
Answer: Main types include manual billing, standalone billing software, cloud‑based online billing, GST‑compliant billing systems, integrated billing and accounting platforms, and industry‑specific billing solutions.
Q2. Which billing system is best for small businesses?
Answer: Cloud‑based billing systems with automated workflows and GST support are usually best for small businesses. They balance affordability with compliance and automation.
Q3. Why is GST compliance important for billing systems in India?
Answer: GST compliance ensures accurate tax calculations, avoids regulatory penalties, and supports proper GST filing and reporting.
Q4. Can billing systems integrate with accounting software?
Answer: Yes. Many modern billing systems sync with accounting platforms so invoices, taxes, and payments update automatically in financial books.
Q5. How do I choose a billing system for my business?
Answer: Evaluate invoice volume, tax needs, automation levels, integration requirements, and scalability. Use a comparison checklist to finalize.